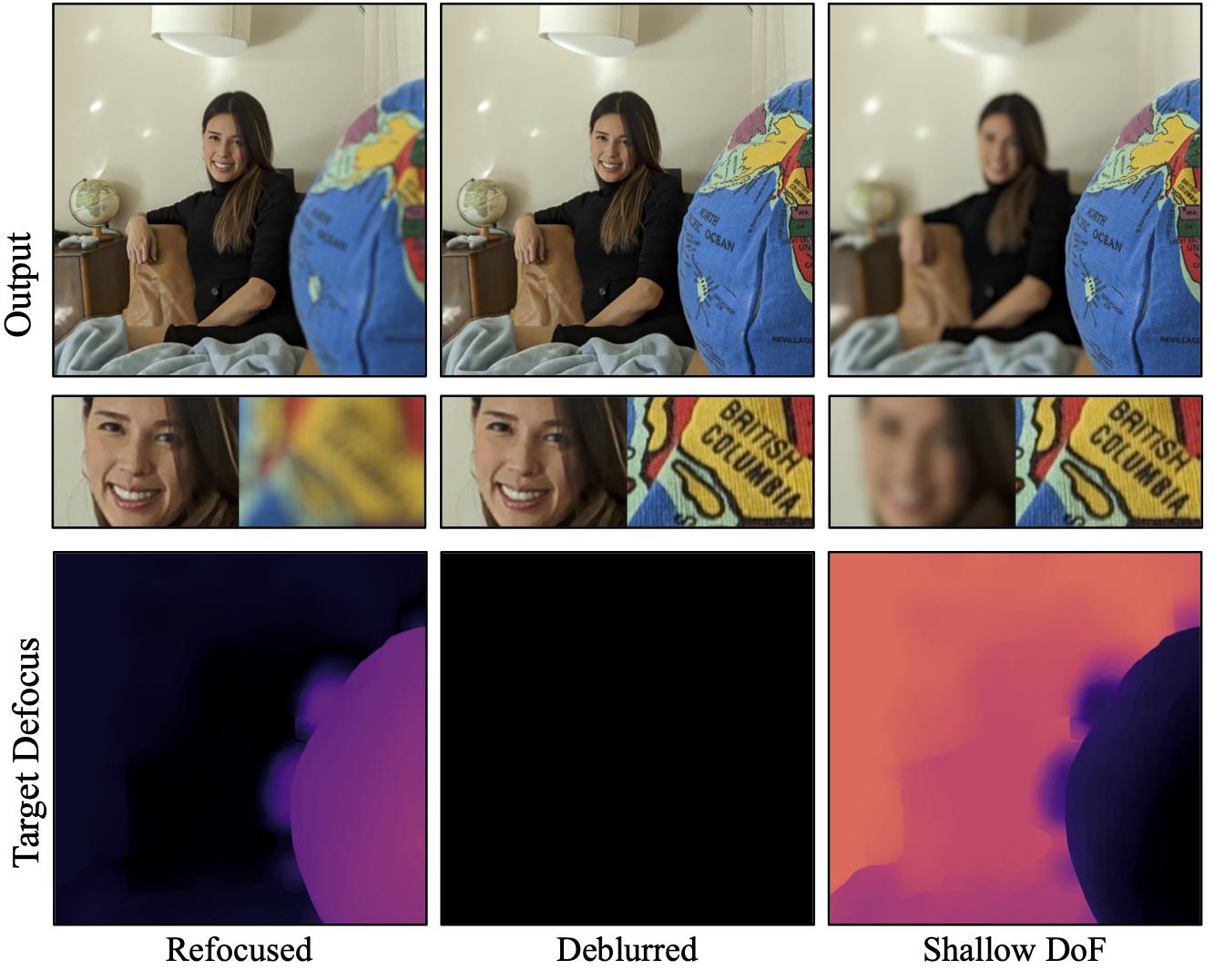
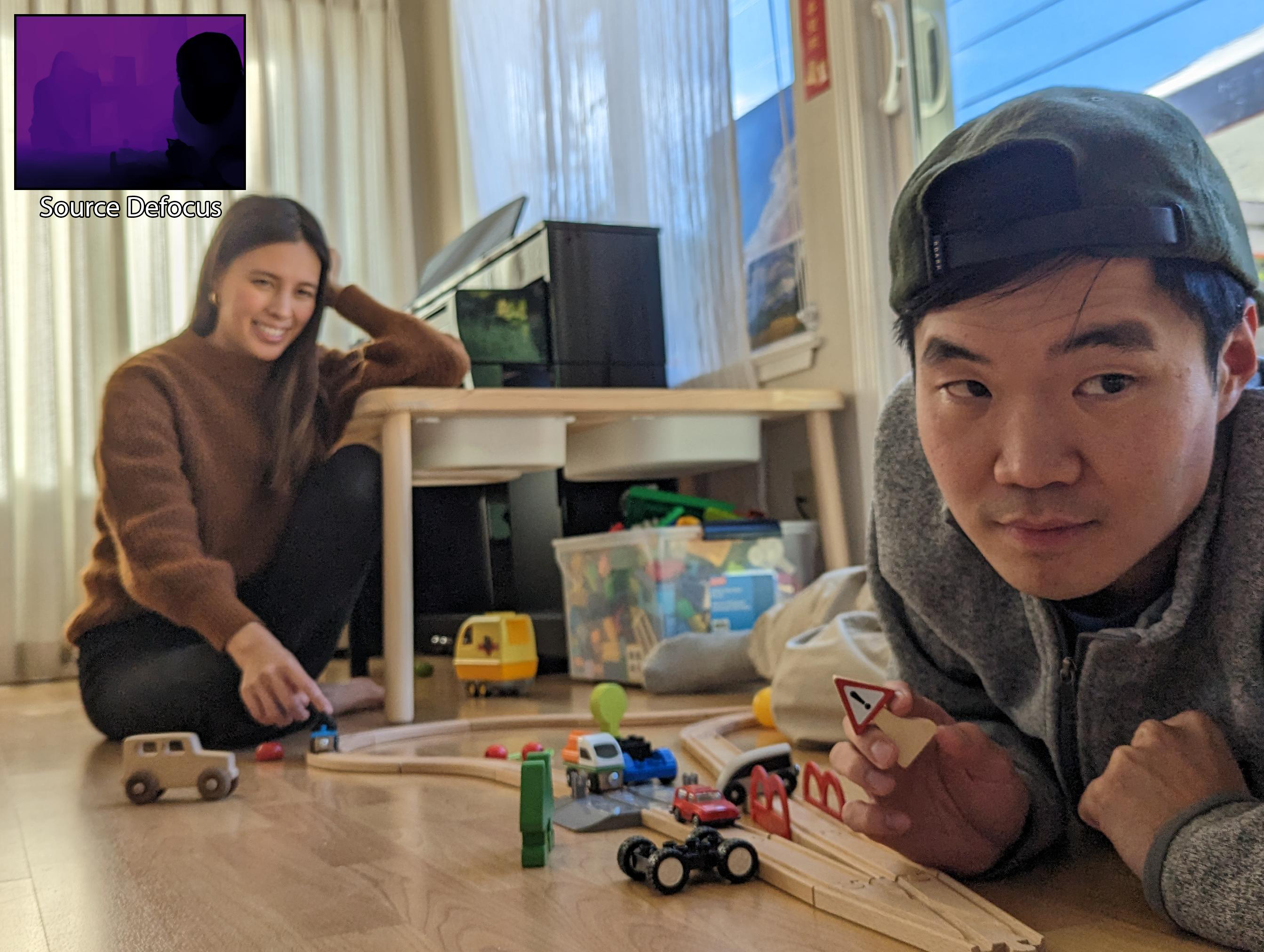
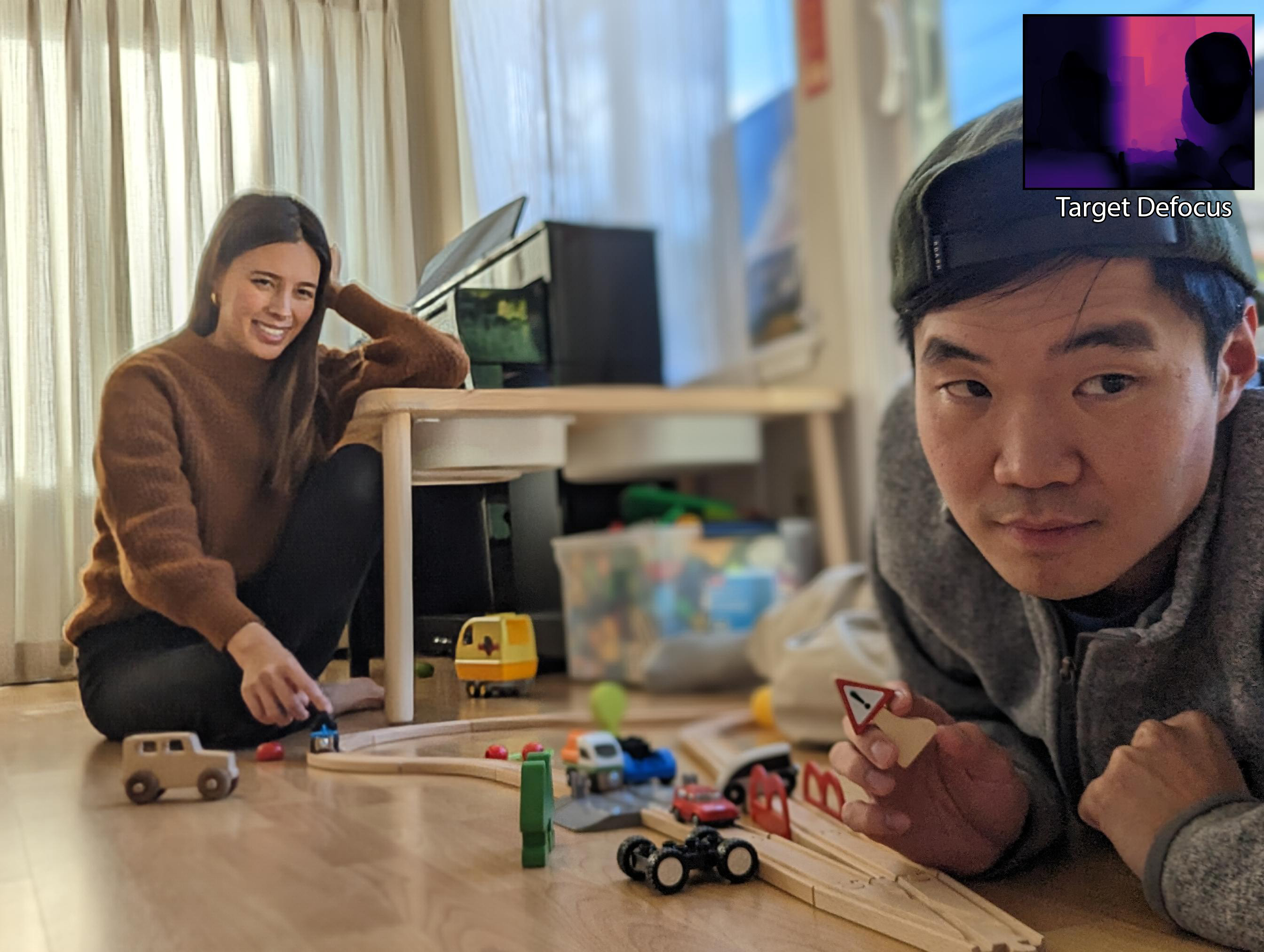
Given a dual camera capture, we can both deblur and add realistic blur to enable complete defocus control including refocusing, aperture control and more.
Here we showcase examples where we simulate changing the focal plane and aperture, and the first frame of each video is the input view.
Please view in full screen for highest quality.
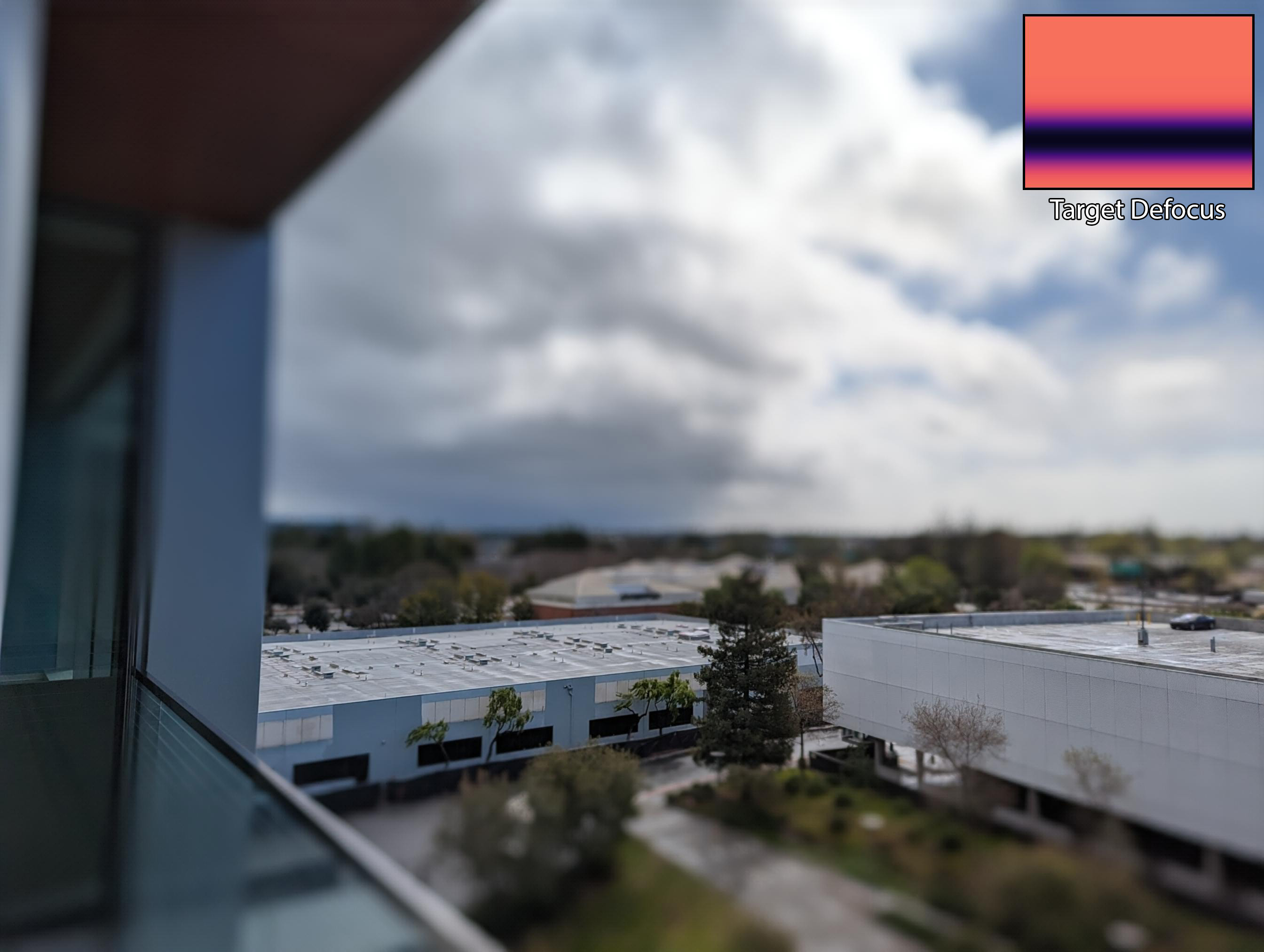
Using a single capture with dual-camera, we can perform post-capture refocus and DoF control by simulating different apertures. Below is the captured frame that is used as an input. You can interactively change the refocus and depth of field to see how our method can be used in the real world.
Click on a subject to refocus
and use the slider for DoF Control
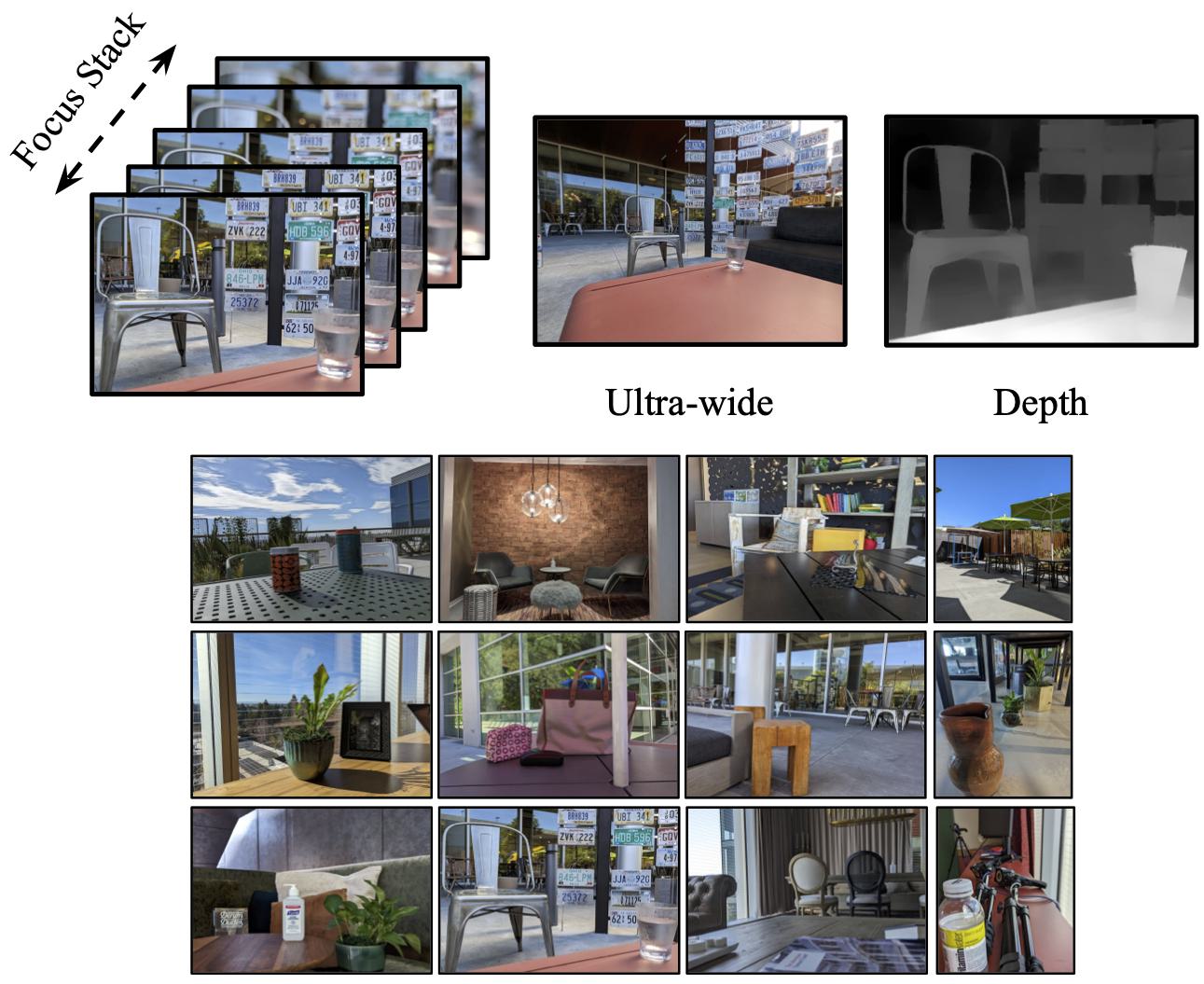
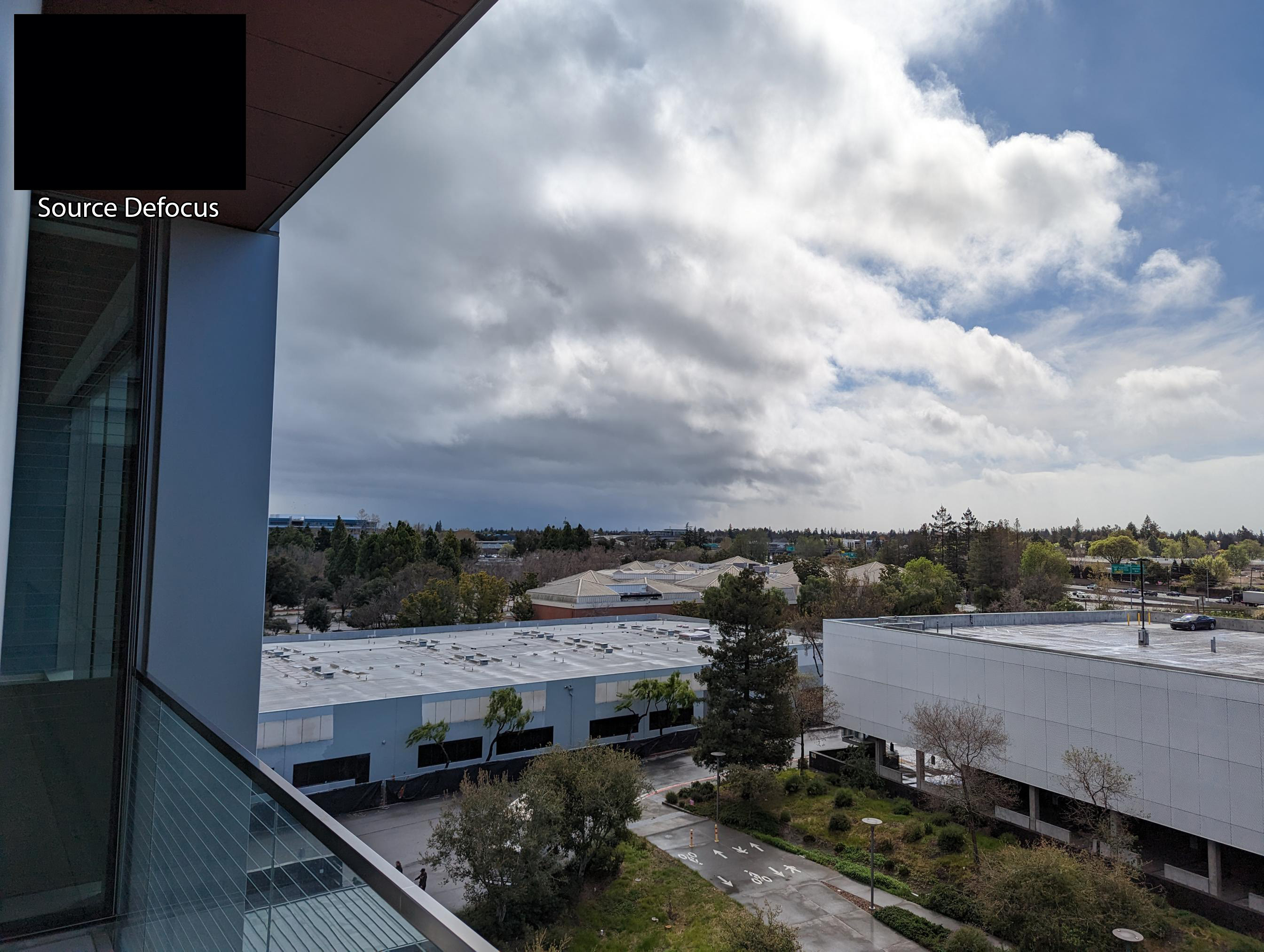
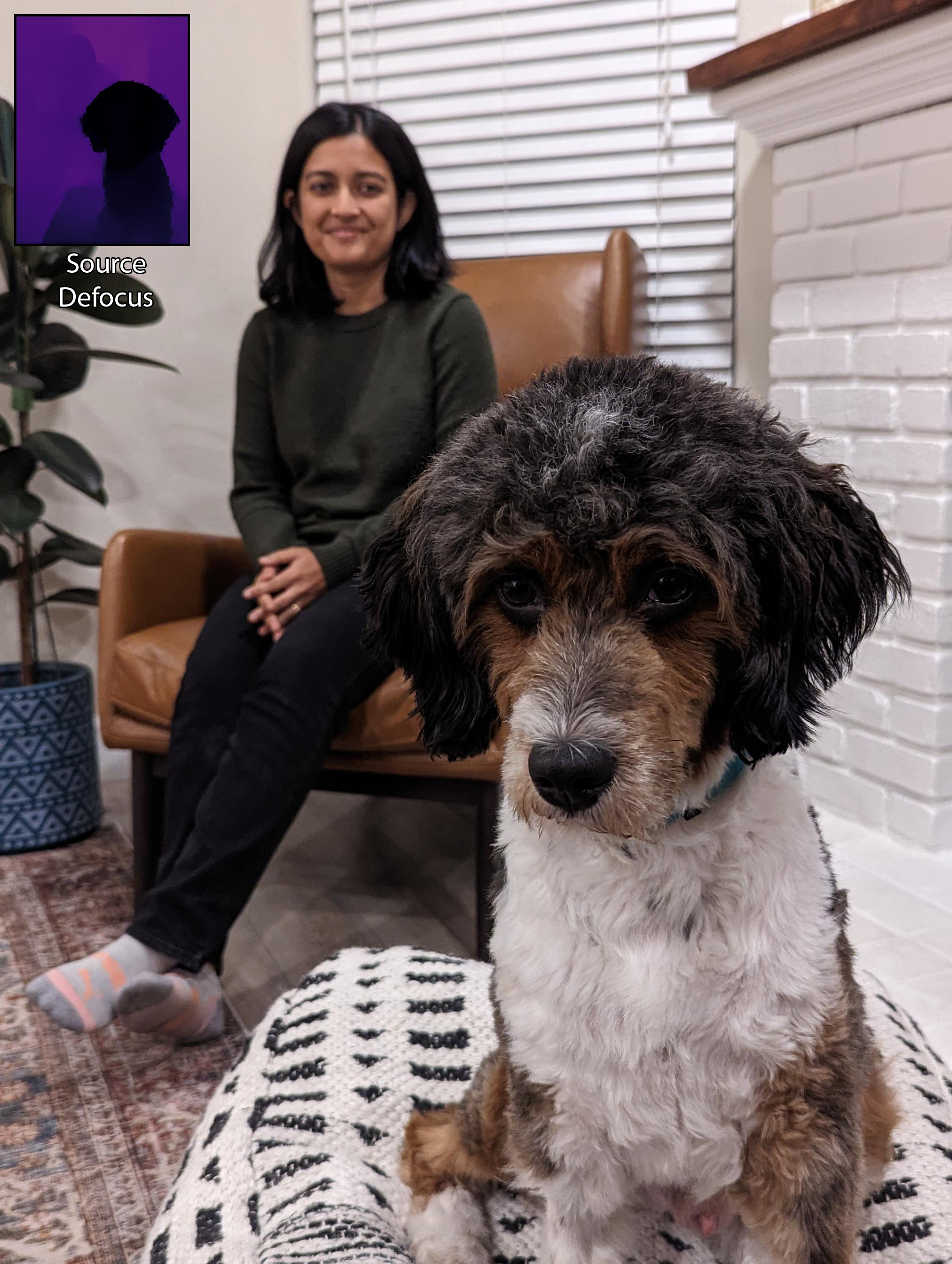
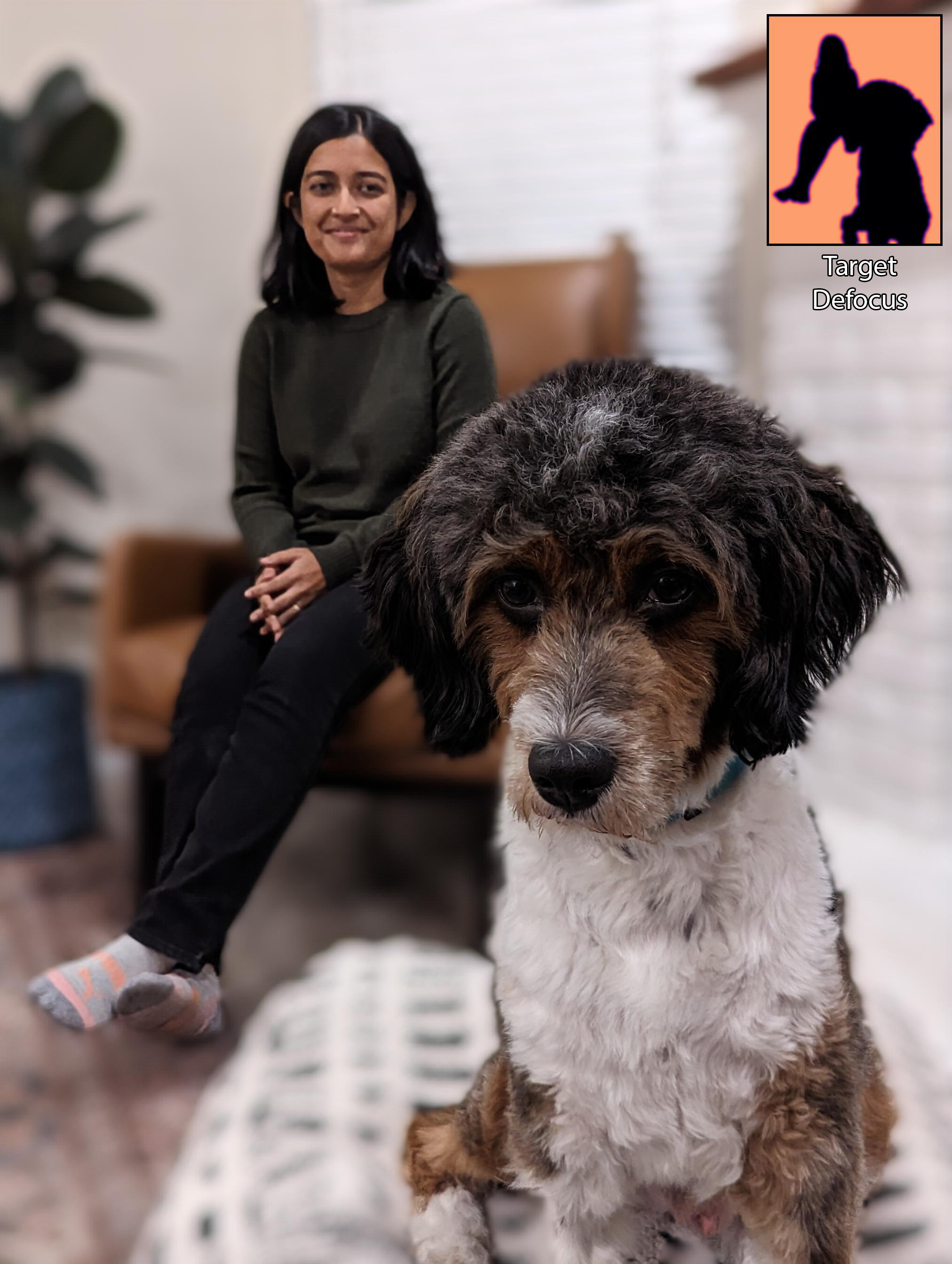
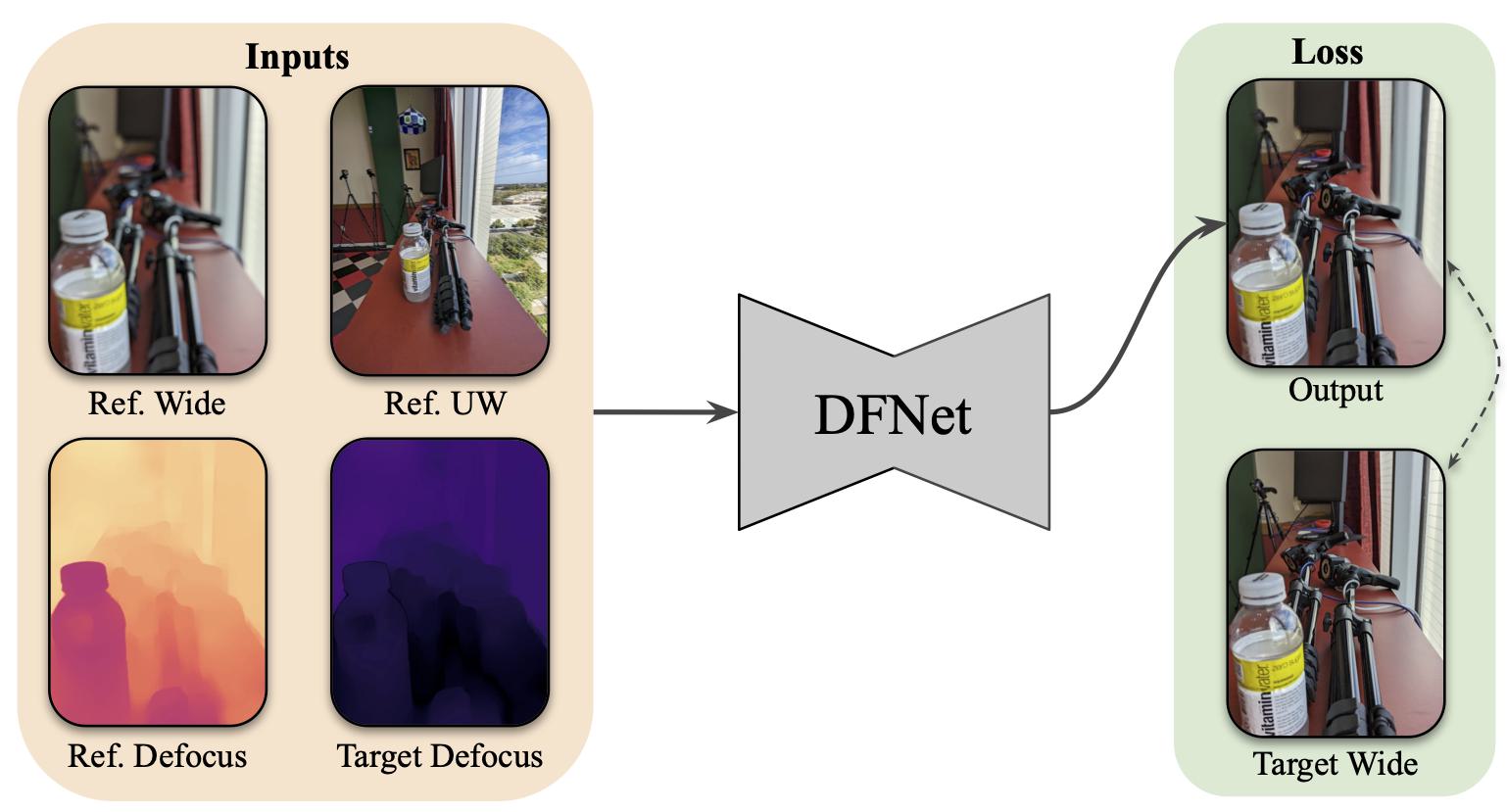
The interactive demo above is using a SINGLE capture with dual-camera. A photo captured with the main camera, also called wide (W), which has high resolution and shallow depth of field (DoF) and a photo from the ultra-wide camera (UW) which has a deep DoF but lower resolution. Our method can combine the two inputs to get a controllable DoF while maintaining high resolution!
Below we show the inputs for this example.
In this work, we propose DC2, a system for defocus control for synthetically varying camera aperture, focus distance and arbitrary defocus effects by fusing information from such a dual-camera system. Our key insight is to leverage real-world smartphone camera dataset by using image refocus as a proxy task for learning to control defocus. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations on real-world data demonstrate our system's efficacy where we outperform state-of-the-art on defocus deblurring, bokeh rendering, and image refocus. Finally, we demonstrate creative post-capture defocus control enabled by our method, including tilt-shift and content-based defocus effects.
















@inproceedings{alzayer2023defocuscontrol,
title={DC2: Dual-Camera Defocus Control by Learning to Refocus},
author={Alzayer, Hadi and Abuolaim, Abdullah and Chun Chan, Leung and Yang, Yang and Chen Lou, Ying and Huang, Jia-Bin and Kar, Abhishek},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
pages={--},
year={2023}
}